The Greek version is HERE
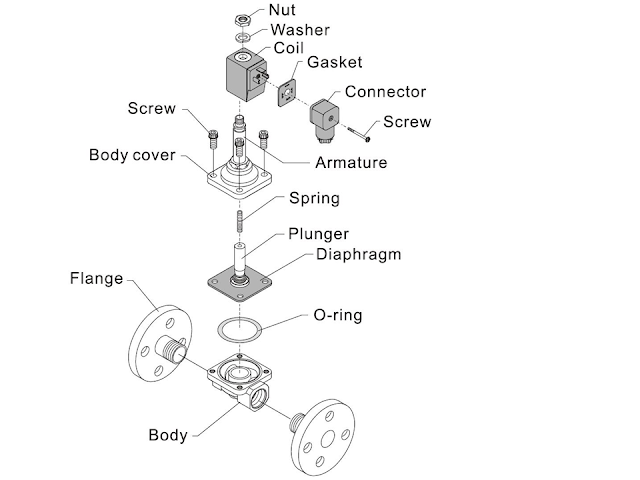
Solenoid valves are the most commonly used fluid control components and are used in many applications. Their function is to stop or allow the flow of liquids or gases.
Power is driven by the motor of the valve cores, solenoid valves (shut-off valve), the valve stem and the control valve. Valves are two-job that is fully open and fully closed, control valve is mounted above the positioner solenoid valve, through dynamic stability of the closed loop regulation to keep the valve in one position. switch: Road through the solenoid valve coil can be on or off, switch when the time is short. Solenoid valve, drives are generally used motor, opening / closing action takes some time to complete the analog, you can adjust.
One of the many applications of electromagnetism is to control the passage of liquids or gases through a tube. The element that does this job is called a solenoid valve or solenoid valve.
A coil that receives a specific and defined voltage generates enough electromagnetic force to pull the iron cylindrical pin that is in the middle of the coil and is connected to the material that plugs or leaves free the passage of gas or liquid.
Analog three-way valve for cold water for space cooling use
If the command is proportional, usually 0 to 10 volts dc and instead of an electromagnet there is a control motor, then the valve can take all intermediate values except fully open or fully closed. In this way the position of the pin can be precisely controlled and consequently e.g. of temperature in an air-conditioned space. There is a wide variety of valves depending on the use, e.g. pressure resistance, pipe dimension (usually measurable in inches), pass material, explosiveness, etc. If the valve is open when the coil is not live, the passage is free and the valve is and is called normaly open. If it is closed it is normaly close. The first photo shows a steam solenoid valve.
Analog steam valve for control of room temperature of production machine. One point of attention is the "burning" of the solenoid coil. If the solenoid valve is energized without its metal part being placed in its socket, ie if it is "in the air", after a short time it will burn due to the greater current that will pass through the coil due to the lack of the iron core - pin . The analog ones need three conductors to control them and the simple two conductors, with the exception of the grounding which is not always necessary at low operating voltages.
Programmable Female Solenoid Valve 1in, BATTERY (IP 68) EN gecom.gr
A coil that receives a specific and certain voltage, creates enough electromagnetic force to pull the iron cylindrical pin (plunger) that is in the middle of the coil and is connected to the material that plugs or leaves free the passage of gas or liquid (membrane).
If the valve is open when its coil is not live, the passage is free and the valve is and is called normaly open . If it is closed it is normaly close.
In this way the position of the pin can be precisely controlled and consequently e.g. of temperature in an air-conditioned space.
The analog ones need three conductors to control them and the simple two conductors, with the exception of the grounding which is not always necessary at low operating voltages.
There is a wide variety of solenoid valves depending on the use, e.g. pressure resistance, pipe dimension (usually measurable in inches), pass material, explosiveness, etc.
The coils are the Achilles heel of the solenoid valves and the quality of their construction is a key feature of the quality of these valves.
The various coils usually operate on 400V, 24V or 12V AC or DC depending on the type of installation we have chosen.
One point of attention is the "burning" of the solenoid coil. If the solenoid valve is energized without its metal part being placed in its socket, that is, if it is "in the air", after a short time it will burn due to the greater current that will pass through the coil due to the lack of iron core - pin .
Solenoid valves can have two or more inlets. In the case of the two inputs-outputs one is input and the other output.
In the case of the three inputs-outputs of the valve the input is made from 2 inputs and the outflow from 1 output.
Three-way solenoid valves are used for two different, alternative services with a common outlet and find application mainly in solar systems, boilers and autonomies.
GAS ELECTROMAGNETIC VALVES
GAS GAS Solenoid ValvesManual Reset, Normally Open (NO) and Normally Closed (NC)
GAS GAS Solenoid Valves are designed to be combined with any
gas detection system which sends a warning signal
when a emergency. All solenoid valves are
reset manually according to the Italian standard for CEI UNI-CIG 70028 gas detection systems.
Operating Principle
Normally Open (NO) During normal operation there is no power consumption and thus no part of the system is subject to wear. There is no annoying buzz or oscillation and energy is saved. However, when voltage is applied to the electromagnetic coil, the closing (closing) mechanism is released.To re-equip the solenoid coil, make sure that the coil has no current and
pull the return handle.
Normally Closed (N. C.)
The structural accuracy of these models guarantees that the gas will be cut off if
the power supply is cut off. An uninterruptible power supply is therefore required to keep it open
valve. As soon as the power supply to the coil is cut off, the valve closes automatically.
To prevent accidental closing, the valves are equipped with a mechanism that ignores
short-term power outages (30 msec). To re-equip the solenoid valve,
make sure the coil has current and pull the return handle.
In practice, in addition to the main components (compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator), the so-called auxiliary components of the refrigeration machine also play an important role. Auxiliary components are installed in the installation for one or more of the following purposes:
1) To protect the installation
2) To improve the efficiency of the refrigeration unit
3) To ensure automatic control of the operation of the installation
4) To create conditions for a more economical operation of the cooling unit
H variety of different types of accessories is too great.
Some of the accessories used by refrigerants are the following:
1) To protect the installation
2) To improve the efficiency of the refrigeration unit
3) To ensure automatic control of the operation of the installation
4) To create conditions for a more economical operation of the cooling unit
H variety of different types of accessories is too great.
Some of the accessories used by refrigerants are the following:
Dryer filter
Moisture or water vapor and foreign microparticles can cause very serious problems in any refrigeration system. Moisture can freeze inside the nozzle of the expansion valve, oxidize metal parts of the system and wet the windings of the electric motor, which, over time, will lead to burning of the electric motor and breakdown of the coolant. On the other hand, foreign microparticles can contaminate the coolant and eventually accumulate in parts of the compressor valves, causing them to malfunction.
Various types of filters - dryers, have been invented and used to remove moisture, water vapor and foreign particles from the coolant.
These instruments have a molded porous core with a high affinity for water. The core contains substances that neutralize any possible acids and remove foreign microparticles from the refrigeration circuit. To achieve maximum protection in the expansion valve and the solenoid valve, the filter-dryer is usually installed in the liquid line just before these two components.

Flow and humidity index
The purpose of these components is to easily determine if the unit is fully charged with refrigerant. When the unit has less refrigerant than normal, bubbles appear in the flow indicator. The bubbles gradually decrease as the amount of refrigerant increases. When the unit is charged with the proper amount of refrigerant, the flow in the indicator becomes continuous without bubbles. The humidity indicator changes color with the presence of moisture in the coolant. Usually, if there is no moisture, the humidity indicator is blue, while if there is moisture, it turns pink. To avoid misunderstandings in changing the color of the humidity indicator, there is always a note on the flow indicator caps that tells us more color represents the presence of moisture in the coolant (Wet) and more indicates coolant free from moisture (Dry).
Solenoid valve
The solenoid valve is a valve that controls the flow of coolant or gas. It is a "open - closed" type valve, automatically activated. Characteristic of the solenoid valve is its very high opening or closing speed. In some cases, however, this rapid movement of the valve can cause a "hydraulic shock". The movement on the valve shaft is given by a magnetic coil, which when actuated lifts the shaft, which is firmly connected to the valve disk.
Solenoid valve operation
Ø The closed valve remains closed until its coil is activated. Then it opens.
. The open valve remains open, as long as it is activated, ie its coil is energized. When the coil is switched off, then the shaft and the valve due to their weight descend and close the passage of the liquid or gas.
The valve is then closed. Care must be taken in the correct installation of the solenoid valve. In particular:
The direction of flow of liquid or gas through the valve must be in the correct direction indicated by an arrow (arc) on the body of the valve or the word "IN". The valve is positioned correctly when the pressure of the liquid or gas helps to keep the valve closed.
Another point that the manufacturers emphasize is the way of choosing the valves. The choice should be made based on the amount (flow) of fluid flow controlled by the valve, and not based on the diameter of the line.
The data that must be given when ordering a solenoid valve are:
1) The type of fluid to be tested (eg Freon R404A)
2) The size of the connectors (eg ¼)
3) The type of connectors (e.g. soldered or threaded - Fleur)
4) The voltage and operating frequency of the coil (eg 220 Volt / 50 Hz)
Note:
The solenoid valve is powered "in series" by a timer. To thank the ELECTRICIANS of the 1st EPAS OAED THESSALONIKI for the amazing technological content and the wonderful articles they publish on their blog.
The solenoid valve is powered "in series" by a timer. To thank the ELECTRICIANS of the 1st EPAS OAED THESSALONIKI for the amazing technological content and the wonderful articles they publish on their blog.